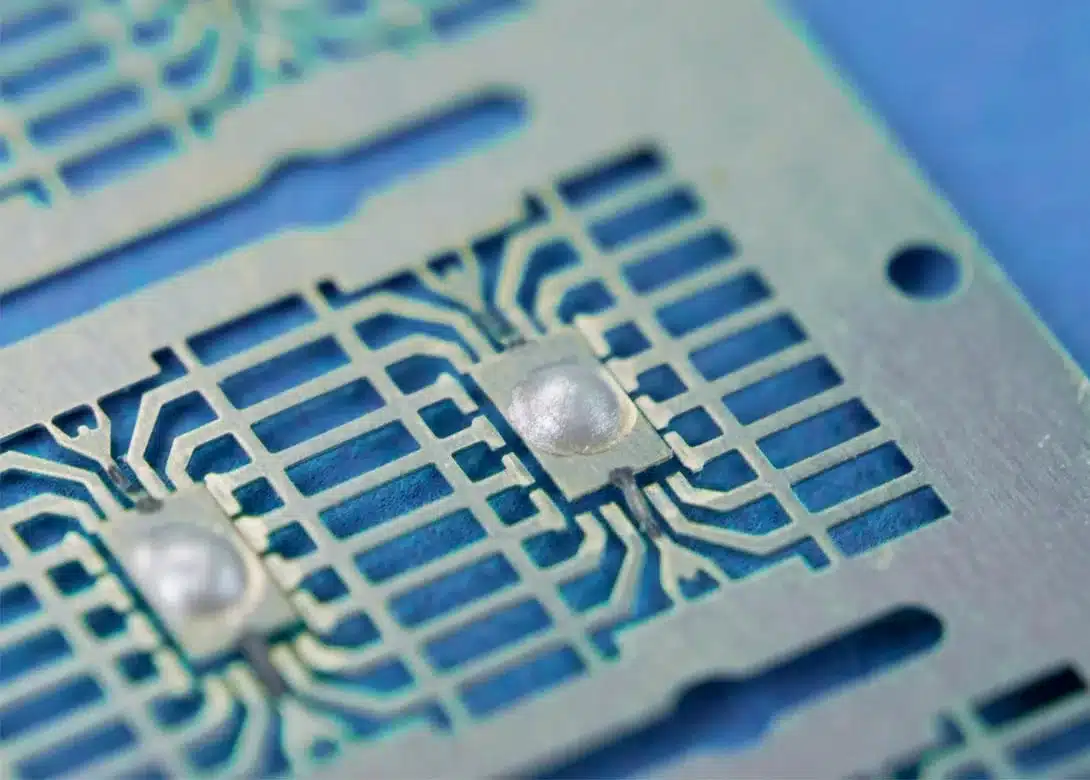
Electrically conductive epoxy is a type of adhesive that not only bonds materials together but also conducts electricity. It is commonly used in various applications where both mechanical bonding and electrical conductivity are required. Here are some key points about electrically conductive epoxy:
Composition and Types
1. Conductive Fillers: These epoxies typically contain conductive fillers such as silver, copper, nickel, or carbon. Silver is the most common due to its excellent conductivity, though it is also the most expensive.
2. Epoxy Resin: The base resin provides the adhesive properties and structural integrity. Epoxy resins are known for their strong bonding capabilities, chemical resistance, and durability.
Properties
1. Electrical Conductivity: The primary feature is its ability to conduct electricity, making it suitable for applications in electronics and electrical engineering.
2. Thermal Conductivity: Many conductive epoxies also have good thermal conductivity, which helps in dissipating heat from electronic components.
3. Mechanical Strength: They offer strong adhesion to a variety of substrates, including metals, ceramics, glass, and some plastics.
4. Chemical Resistance: Epoxy resins provide good resistance to chemicals and environmental factors, ensuring long-term stability and performance.
Applications
1. Electronics Assembly: Used for attaching components to printed circuit boards (PCBs), such as capacitors, resistors, and integrated circuits.
2. EMI/RFI Shielding: Provides electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) shielding in electronic enclosures and devices.
3. Repair and Maintenance: Used in the repair of damaged conductive paths in electronic devices.
4. Heat Sinks: Bonding heat sinks to electronic components to ensure efficient heat transfer.
5. Sensors and Antennas: Used in the fabrication and assembly of various sensors and antennas that require both mechanical bonding and electrical connectivity.
Advantages
1. Precision Application: Can be applied precisely where needed, reducing waste and ensuring efficient use of materials.
2. Versatility: Can bond a wide range of materials, making it suitable for diverse applications.
3. Improved Reliability: Enhances the reliability and longevity of electronic assemblies by providing strong, conductive bonds.
Considerations
1. Cost: Conductive fillers like silver make these epoxies relatively expensive however generally reduces capital expense costs such as solder reflow ovens.
2. Curing Time: The curing process may require specific conditions (e.g., temperature and time) to achieve optimal properties.
3. Handling and Storage: Requires careful handling and storage to maintain its conductive properties and adhesive performance.
When selecting an electrically conductive epoxy, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your application, such as the level of conductivity needed, the materials to be bonded, and environmental conditions.